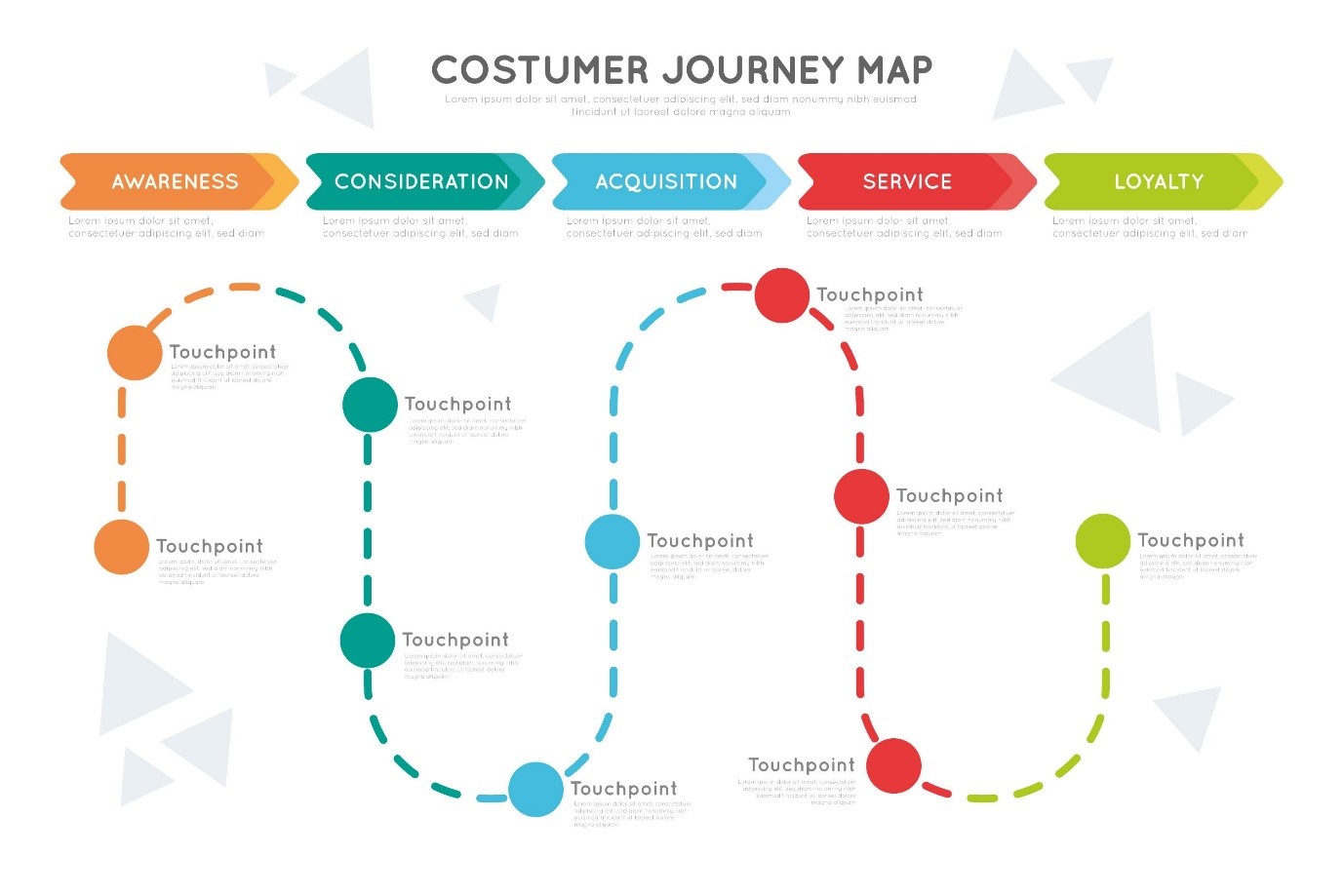
Customer journey mapping is hot stuff these days, and for good reason: A great customer journey translates itself into sales that don’t require selling.
Sales without selling?
Yes, we’re talking customer loyalty.
Nail this, and you’ve found yourself a hen that lays golden eggs.
In short: An outline of a customer’s journey provides a blueprint of a customer’s behavior – their needs, motivations and concerns and is the sum of all the possible interactions that an individual might have with the brand.
Customer journeys may consist of start-to-finish experiences that culminate in a purchase or brand evangelism, or they might constitute one-off interactions with your brand that don’t go any further.
The key thing to keep in mind is that a customer journey map accounts for all possible types of experiences, big and small, from the perspective of the customer.
“In what stage of the customer journey are we operating with this campaign?”
Why Is Customer Journey Mapping Important?
There’s no benefit in understanding something you’ll never use. Here are some reasons why you should deep-dive into this matter right away:
- It explains how customers are interacting with your business– Customer journey maps enable a bird’s eye view of their interaction with your business from their perspective. Unexpected insights will arise.
- It highlights what your customers need (or expect) – and when they need it at different stages of the sales funnel/buyer lifecycle.
- It clarifies customer needs and pain-points – The research phase of putting together a customer journey map involves building detailed customer profiles which will uncover a range of needs and pain-points, across the whole customer experience, that you might not have considered.
- It shows you shortcomings in your current customer journey – Very few businesses have perfect customer journeys. Customer journey maps show you exactly which touchpoints are missing, underdeveloped, and underperforming.
- It maps optimization and development priorities – Along with highlighting problems, customer journey maps can also be used to set priorities.
- And last but not least: It enables you to target resources for maximum returns.
What Are the Stages in a Customers Journey?
The stages of a customer journey aren’t set in stone. Most of the time however, your customers will follow a certain process when they interact with you and your product or service.
Below, we’ve outlined the most common steps:
- Awareness – It all starts here: Awareness is where consumers start to become familiar with your brand. They’re in the midst of researching you, and now know little about your brand and what you do.
- Consideration – In a second phase, prospective customers begin to consider you as a viable option. You can give them more information by delivering meaningful and valuable content using blogs, webinars, demos, case studies and videos. This content tells your audience that you’re worth investing in and sets you up as a thought leader.
- Purchase – If you want your consumers to recommend you, you’ll have to deliver actual value. A happy customer will reward you with positive Word-Of-Mouth, and, further purchases of course!
- Retention – Loyal, returning customers offer a lot more value than a new user who has to go through the onboarding process (costing you big bucks), and who may or may not stick with you. Offering valuable customer support, rewards, discounts, follow-ups and gathering feedback to make sure you’re still doing everything right can help retain customers.
- Advocacy – Positive Word-Of-Mouth is one of the most powerful forms of marketing and it is tough for most brands to achieve this status. So, if you manage to acquire this position, you must keep your customers as brand advocates and then aim to increase your customer base by drawing in new leads.
Okay, okay, but how do I manage all of this?
Through nurturing your customers to the fullest; paying close attention to their needs and wants and offering them continued support and value as their progress through your map.
Wait… what map? I don’t have one yet!
“Can you give me a short overview of your ideal customer journey?”
Writing Your Ideal Customer Journey Map
We know, talk is cheap.
Let us help you get started with step-by-step guide:
- Step 1: Build Customer Profiles – Look at the data!
- Step 2: Define General Stages – Awareness, Consideration, Decision & Loyalty
- Step 3: Attach Goals to Each Stage – What are the customer’s goals?
- Step 4: Identify Touchpoints for Each Stage – Outline any way that a customer might interact with your brand
- Step 5: Identify Moments of Truth – A key moment of truth is when a customer decides to buy
- Step 6: Identify Drop-Off Points and Goal Completion – Where are customers successfully completing their journey?
- Step 7: Gather Supplementary User Feedback – Gather additional feedback
- Step 8: Identify Areas for Improvement and “Amplification” – Highlight the most problematic areas on your map and prioritize them
- Step 9: Compare Competitor Maps – How do competitor customer journeys compare to yours?
- Step 10: Develop and Test New Ideas – CJM’s are an excellent way of ensuring a continuous flow of options for testing and split-testing
Customer Journey Mapping provides the magnifying glass that allows you to take a deeper look into the intricacies of each consumer-brand interaction. Even more, it provides insights into your customers emotions, requirements and their potential decisions, which will enable you to streamline your marketing strategy. If you haven’t started mapping out your own customer journey, you’re leaving money on the table.
Don’t feel like doing it by yourself, or in need of ideas for improving your customers journey? With over 18 years of experience, Transmyt can help you attract and retain the customers you deserve.
Want more insights?
Subscribe to our weekly marketing tips and advice, delivered straight to your inbox.
Oops! We could not locate your form.
Keep Reading
Want more? Here are some other blog posts you might be interested in.
The MVP—Minimum Viable Product—has become gospel in startup circles. Build fast, test fast, fail fast. But in today’s crowded market, viability ...
The startup myth goes like this: work 20-hour days, pivot constantly, chase the high of the new. That’s what makes a ...
Most founders build their first leadership teams for speed, comfort, and alignment. Understandably, you’re strapped for time and need people who ...
For founders and growing companies
Get all the tips, stories and resources you didn’t know you needed – straight to your email!